
Contributions
Abstract: PB1685
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
The current situation of maintenance (MT) after front-line therapy in non-transplant patients with multiple myeloma (MM) is not adequate in China.
Aims
We conducted this multi-centered retrospective real-world study on efficacy and safety of the mainstream maintenance regimens, thalidomide (T-MT), lenalidomide (L-MT) and bortezomib (B-MT).
Methods
Clinical data of newly diagnosed MM patients were collected from 6 centers of North China MM Registry from January 2010 to May 2020. The progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS) from maintenance, and drug toxicities were compared in T-MT, L-MT and B-MT groups.
Results
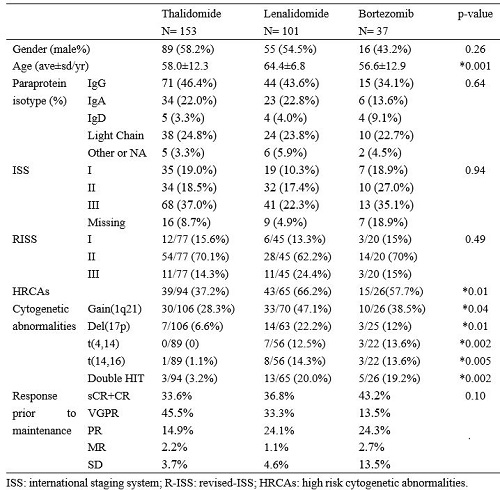
A total of 291 patients were enrolled, including 153 in T-MT, 101 in L-MT and 37 in B-MT. At baseline, the gender ratio, paraprotein isotype, ISS and R-ISS, as well as response evaluation before MT were comparable (Figure 1). Patients on L-MT were older than the other groups. Meanwhile, greater proportions of patients on L-MT and B-MT had high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities (HRCA), defined as amplification 1q21 (1q21+), deletion 17p (17p-), t(4,14), t(14,16), or dual HRCAs (double hit).
The median follow-up duration since maintenance was 35.6, 19.4 and 17.3 months (m) in T-MT, L-MT and B-MT groups, respectively. Disease progression was recorded in 95 patients (62.1%) with T-MT, 49 (48.5%) with L-MT and 13 (35.1%) with B-MT. While mortality was 43(28.1%), 20(19.8%) and 2(5.4%), respectively. The median PFS was 22.5m in T-MT, as compared with 20.0m in L-MT and 37.0m in B-MT (p=0.61). Median OS was 79.5m in T-MT, whereas not reached (NR) in the others (p=0.21).
Patients reaching complete response (CR) or stringent CR (sCR) before MT had significantly prolonged PFS compared to those with very good partial response (VGPR) or less in T-MT (28.0m vs 16.1m, p=0.02) and L-MT groups (27.0M vs 13.2M, p=0.01), while comparable in B-MT (NR vs 16.5m, p=0.36). Meanwhile, patients in each cohort had similar OS despite of different response before MT.
Patients with 1q21+ on T-MT had shorter median PFS compared to those without (16.1m vs 22.5m, p=0.14), so did impaired median OS (52.3m vs 96.5m, p= 0.003). While PFS was similar in patients with 1q21+ or without in L-MT group (33.5m vs 17.9m, p=0.29), and 4-year estimated OS was 52% and 51%(p=0.99). 1q21+ or not did not affect PFS in B-MT (15.2m vs 16.5m, p=0.89) , and OS was not reached.Only a few patients with 17p- in T-MT and B-MT, yet presented remarkably inferior PFS (6.7m vs 22.5m, p=0.007) and OS (39.6m vs 79.5m, p=0.02) with T-MT. As for L-MT, PFS (15.4m vs 27.0 m, p=0.33) and OS (37.6m vs NR, p=0.99) were not of discrepancy between 17p- or without.In patients with any adverse CA, T-MT resulted in impaired PFS (11.9m vs 20.9m, p=0.06) and OS (52.3m vs NR, p<0.01). In contrast, PFS and OS were both comparable in L-MT or B-MT, no matter with HRCA or not.
The main reason of maintenance withdrawal was disease progression. Adverse event related discontinuation was seen in 5.3%, 6.1% and 0 patients in T-MT, L-MT and B-MT.
Conclusion
In this multi-centered real-world study, thalidomide, lenalidomide or bortezomib as maintenance after front-line therapy in non-transplant NDMM patients suggest that a response of CR or better predicts superior PFS. HRCAs drag down survival in T-MT, while L-MT and B-MT mostly reverse the negative effects. Although patients on L-MT and B-MT have greater proportion of HRCAs, PFS in three groups are comparable. Clinicians in real practice prefer to select lenalidomide or bortezomib as maintenance in high-risk patients.
Keyword(s): Maintenance, Multiple myeloma
Abstract: PB1685
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies - Clinical
Background
The current situation of maintenance (MT) after front-line therapy in non-transplant patients with multiple myeloma (MM) is not adequate in China.
Aims
We conducted this multi-centered retrospective real-world study on efficacy and safety of the mainstream maintenance regimens, thalidomide (T-MT), lenalidomide (L-MT) and bortezomib (B-MT).
Methods
Clinical data of newly diagnosed MM patients were collected from 6 centers of North China MM Registry from January 2010 to May 2020. The progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS) from maintenance, and drug toxicities were compared in T-MT, L-MT and B-MT groups.
Results
A total of 291 patients were enrolled, including 153 in T-MT, 101 in L-MT and 37 in B-MT. At baseline, the gender ratio, paraprotein isotype, ISS and R-ISS, as well as response evaluation before MT were comparable (Figure 1). Patients on L-MT were older than the other groups. Meanwhile, greater proportions of patients on L-MT and B-MT had high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities (HRCA), defined as amplification 1q21 (1q21+), deletion 17p (17p-), t(4,14), t(14,16), or dual HRCAs (double hit).
The median follow-up duration since maintenance was 35.6, 19.4 and 17.3 months (m) in T-MT, L-MT and B-MT groups, respectively. Disease progression was recorded in 95 patients (62.1%) with T-MT, 49 (48.5%) with L-MT and 13 (35.1%) with B-MT. While mortality was 43(28.1%), 20(19.8%) and 2(5.4%), respectively. The median PFS was 22.5m in T-MT, as compared with 20.0m in L-MT and 37.0m in B-MT (p=0.61). Median OS was 79.5m in T-MT, whereas not reached (NR) in the others (p=0.21).
Patients reaching complete response (CR) or stringent CR (sCR) before MT had significantly prolonged PFS compared to those with very good partial response (VGPR) or less in T-MT (28.0m vs 16.1m, p=0.02) and L-MT groups (27.0M vs 13.2M, p=0.01), while comparable in B-MT (NR vs 16.5m, p=0.36). Meanwhile, patients in each cohort had similar OS despite of different response before MT.
Patients with 1q21+ on T-MT had shorter median PFS compared to those without (16.1m vs 22.5m, p=0.14), so did impaired median OS (52.3m vs 96.5m, p= 0.003). While PFS was similar in patients with 1q21+ or without in L-MT group (33.5m vs 17.9m, p=0.29), and 4-year estimated OS was 52% and 51%(p=0.99). 1q21+ or not did not affect PFS in B-MT (15.2m vs 16.5m, p=0.89) , and OS was not reached.Only a few patients with 17p- in T-MT and B-MT, yet presented remarkably inferior PFS (6.7m vs 22.5m, p=0.007) and OS (39.6m vs 79.5m, p=0.02) with T-MT. As for L-MT, PFS (15.4m vs 27.0 m, p=0.33) and OS (37.6m vs NR, p=0.99) were not of discrepancy between 17p- or without.In patients with any adverse CA, T-MT resulted in impaired PFS (11.9m vs 20.9m, p=0.06) and OS (52.3m vs NR, p<0.01). In contrast, PFS and OS were both comparable in L-MT or B-MT, no matter with HRCA or not.
The main reason of maintenance withdrawal was disease progression. Adverse event related discontinuation was seen in 5.3%, 6.1% and 0 patients in T-MT, L-MT and B-MT.

Conclusion
In this multi-centered real-world study, thalidomide, lenalidomide or bortezomib as maintenance after front-line therapy in non-transplant NDMM patients suggest that a response of CR or better predicts superior PFS. HRCAs drag down survival in T-MT, while L-MT and B-MT mostly reverse the negative effects. Although patients on L-MT and B-MT have greater proportion of HRCAs, PFS in three groups are comparable. Clinicians in real practice prefer to select lenalidomide or bortezomib as maintenance in high-risk patients.
Keyword(s): Maintenance, Multiple myeloma


